
Concept
Archiving Overview
Archiving is the process of preserving historical data, which is comprised of selected events and extended trend logs. For example, some facilities are required to maintain archives to comply with government regulations. Another example is in secure facilities where they must maintain records of who logged in or who changed setpoints. Archiving is not a backup function because archive data cannot be imported back into the system.
Archiving is a function of an Enterprise Server. Therefore, you cannot archive data on a standalone SmartStruxure server device. However, you can archive trend logs and extended trend logs created on a SmartStruxure server device that are monitored by extended trend logs created on an Enterprise Server.

The Enterprise Server Windows service runs under the System account of the local machine, or a another custom account, where the Enterprise Server is installed. If you plan to save the archive files to a network drive, make sure that the System acccount or the custom account is given write access to this drive to ensure that the archive process can validate the path and then save the files to that location.
The system archives historical data into two types of log files:
Event logs: All the selected alarm, user activity, and system events are archived into one file.
action_zoom_plus_stroke 
Extended trend logs: The system archives data collected from selected extended trend logs created on the Enterprise Server.
action_zoom_plus_stroke 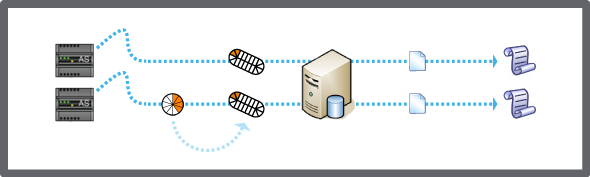
Archiving Formats and Storage
You generate an archive by selecting either a CSV or XML format. You can store the archive in Enterprise Server or define a different location.
For more information, see Archiving Formats and Storage .
Archive Folders, Files, and Names
The archving process creates uniquely named folders to identify the type of archive (manual or scheduled) and the date on which the archive was performed. Each folder includes the log files that were archived on that date.
For more information, see Archive Folders, Files, and Names .
Archiving Server Compatibility
You can configure archiving on an Enterprise Server.
For more information, see Archiving SmartStruxure Server Compatibility .
System Alarms for Archiving
There are several default system alarms for archiving.
For more information, see System Alarm ID List .
Manual and Scheduled Archiving
You can archive data as needed using manual methods or at predefined intervals using a schedule.
For more information, see Manual and Scheduled Archiving .
 Archiving SmartStruxure Server Compatibility
Archiving SmartStruxure Server Compatibility
 Archiving Formats and Storage
Archiving Formats and Storage
 Archive Folders, Files, and Names
Archive Folders, Files, and Names
 System Alarm ID List
System Alarm ID List
 Manual and Scheduled Archiving
Manual and Scheduled Archiving
 Extended Trend Logs
Extended Trend Logs
 How Events Work
How Events Work