Log on to rate and give feedback
1
2
3
4
5
Log on to rate
0

Explicación de procesos
Productos
AS-C, AS-B, Enterprise Server, AS-P, Project Configuration Tool
Funcionalidades:
Funcionalidad básica
Versión del producto:
1.9
14/12/2016
Saving a Search
You save a search so you can reuse it later.
To save a search
In WorkStation, in the search box, enter the search criterion.
In the In folder box, enter the reference type and the folder or container object in which you want to perform the search:
~ searches in the specific folder or container object
../.. searches one level up from where the Search object is saved
On the Search toolbar, click the Save search criteria button
.action_zoom_plus_stroke 
action_zoom_plus_stroke 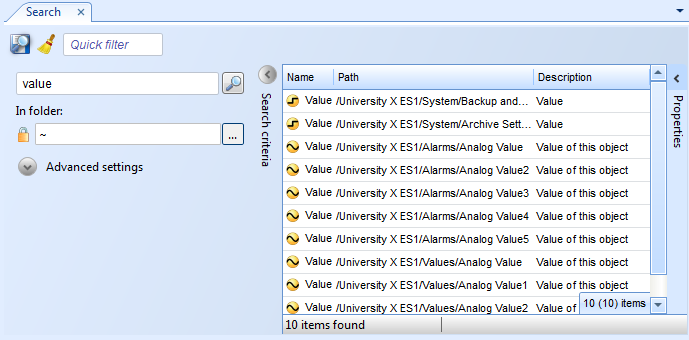
Select the path where you want to save the Search object.
In the Name box, type a name for the Search object.
Click Save .
 Search Overview
Search Overview
 Search View
Search View
 Search View Toolbar
Search View Toolbar