
Concept
MS/TP Cable Routing
The MS/TP network cable should be routed in a continuous daisy chain bus configuration. There should not be any Stub connections, Stars or Ring configurations. The bussed cable should pass through each node and be connected with no splits or branches in the cable network.
The following network configuration diagrams (with red Xs) show undesirable arrangements of the connected copper cabling.

You can use repeaters to achieve the star, distributed star (backbone with clusters) and stubs off of the backbone. The repeater separates the cable, while each side (or each port on a multi-port repeater) starts a new wire segment. This avoids the effect of stub or cluster/lump capacitance from distorting the data on the backbone.
No more than 2 repeaters should separate any two nodes on the network. This means after you use a repeater to drop a branch leg off the backbone at multiple locations, you cannot add another repeater on any of these branches because this would create a 3 repeater string to one or more nodes on the network.
With RS-485 MS/TP (or Modbus) communications, two conductors are used to pass the differential data (A+ and B- signals) from one node to the next. To maintain the balanced characteristics between the two wires, the cable must provide twisted pairs and be specified for data communications. As the twisted pair passes alongside other cables and equipment in the facility, there are a multitude of noise sources, radiated EMI and electromagnetic fields that will impose noise onto the twisted pair cable.
Although it is definitely the most important characteristic, the balanced performance of the cable requires more than just the twisted pair characteristic. The twisted pair cable can become unbalanced when encountering discontinuities in the capacitance between the two wires, or the capacitance from conductor to shield or the impedance of the wires. This makes it important to select quality cable specified for RS-485 data communications.
The cable supplier must provide a cable specification that includes all of the characteristics listed in the following tables. The recommended specs for these characteristics are listed and provide the best results.
You should avoid cable where the manufacturer/supplier cannot provide the full cable specifications.
|
Characteristics |
Recommendation |
|
Type |
Shielded Twisted Pair Low Capacitance |
|
Twisted Wire Size |
22AWG - 24AWG |
|
Impedance |
120 Ohms |
|
Capacitance (wire to shield) |
<25 picofarads per foot |
|
Capacitance (wire to wire) |
<14 picofarads per foot |
|
Maximum Length |
Up to 4000 ft max Depending on termination and bias restrictions |
|
Manufacturer |
Model |
Size (AWG) |
Pairs |
Imp. |
Cap1 pf/ft a |
Cap2 pf/ft b |
Vel |
Ple- num |
|
Belden |
3105A |
22 Str |
1 |
120 |
11 |
20.9 |
78% |
|
|
Belden |
3107A |
22 Str |
2 |
120 |
11 |
20.9 |
78% |
|
|
Belden |
9841 |
24 Str |
1 |
120 |
12.8 |
23 |
66% |
|
|
Belden |
9842 |
24 Str |
2 |
120 |
12.8 |
23 |
66% |
|
|
Belden |
82841 |
24 Str |
1 |
120 |
12 |
22 |
76% |
Y |
|
Belden |
82842 |
24 Str |
2 |
120 |
12 |
22 |
76% |
Y |
|
Belden |
89841 |
24 Str |
1 |
120 |
12 |
22 |
76% |
Y |
|
Belden |
89842 |
24 Str |
2 |
120 |
12 |
22 |
76% |
Y |
|
Alpha Wire |
6453 |
22 Str |
1 |
120 |
11 |
20.9 |
78% |
|
|
Alpha Wire |
6455 |
22 Str |
2 |
120 |
11 |
20.9 |
78% |
|
|
Alpha Wire |
6412 |
24 Str |
1 |
120 |
12.8 |
23 |
|
|
|
Alpha Wire |
6413 |
24 Str |
2 |
120 |
12.8 |
23 |
|
|
|
General Cable |
C0841A |
24 Str |
1 |
120 |
14.2 |
25.6 |
66% |
|
|
General Cable |
C0842A |
24 Str |
2 |
120 |
11.4 |
20.5 |
66% |
|
|
Connect-Air |
W241P2050FRIB |
24 Str |
1 |
120 |
10.9 |
19.6 |
78% |
Y |
|
Connect-Air |
W221P2010FRIB |
22 Str |
1 |
120 |
10.9 |
19.6 |
78% |
Y |
- Cap1 = Capacitance between the two conductors of the pair(s)
- Cap2 = Capacitance from each signal conductor to shield
The MNB series controllers use an isolated RS-485 transceiver that requires a network bias. (This is true only for the Automation Server (AS-SMK) and not the AS-P (AS-P-SMK)).
The bias consists of a pull-up resistor to 5V (on the TX/RX+ signal) and a pull-down resistor to ground (on the TX/RX+ signal). The purpose of the bias is to ensure a high-level, data condition exists in the quiescent or idle state when no controller is driving the bus.
The MNB-300 controller provides internal bias jumpers to optionally enable the biasing of the network. To accommodate the full network length of 4000 feet, bias is needed at each end of the bus. With a network of 500 feet or less, the bias can be supplied from one location.
When MNB-300 controllers are not used on the network, or not positioned on the end of the bus (or within 200 feet), the external 5V supply can be used to bias the network.
You can use the VR1TM5 power supply module to provide 5 volt bias for the MS/TP network for the MNB controllers needing the bias. You use one of the 24 VAC transformers listed in this guide to provide power to the supply module. For more information, see Transformers .
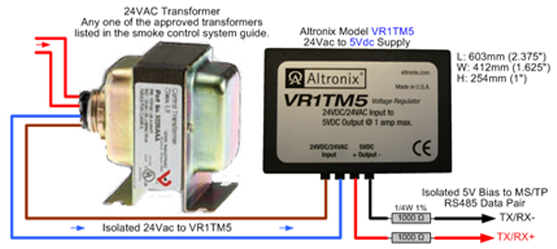
You connect the +5 volt and common outputs from the module to two separate 1K ohm ¼ watt resistors. For the resistor connecting to the supply common, connect the other side of that resistor to the TX/RX- network signal. For the resistor connecting to the supply +5 volt output, connect the other side of that resistor to the TX/RX+ network signal. You use two of the bias modules to connect one at each end of the network to accommodate the full 4000 feet length.

 SmartStruxure Module Installation
SmartStruxure Module Installation
 Terminal Base Installation
Terminal Base Installation
 Power Rating
Power Rating
 Terminal Base Wiring
Terminal Base Wiring
 Electronics Module Installation
Electronics Module Installation
 PS-24V Power Supply Module
PS-24V Power Supply Module
 Automation Server Installation
Automation Server Installation
 AS-P Installation
AS-P Installation
 Module Status LEDs
Module Status LEDs
 I/O Module Installation
I/O Module Installation