
Concept
Grounding and Power for Systems with RP-IO Modules
This section provides grounding and power recommendations for system configurations with the RP-IO I/O modules, which support 24 VAC/VDC input power and have a full-wave rectified and isolated built-in power supply.
For more information, see RP-IO Models .
You can use one local transformer for each RP-IO module (with its connected devices) to minimize any problems with ground loops and disturbances.
Use the following recommendations to design a good working system:
If there are one or more non-isolated external devices, the ground connection is achieved through these devices (terminal 23 in the figure below).
If there are no non-isolated external devices, the incoming G0 may be connected to any of terminals 3, 4, or 5.
The fuse (circuit breaker) F11 must be rated 3 A or higher.
An external Signal Ground Rail (SGR) is not needed.
Every wire is an impedance, and current through an impedance results in a voltage that is proportional to the current. Such a voltage introduces disturbances to the signal. Thus:
For external devices not internally connected to G0, use the corresponding RET connections rather than terminals 3, 4, or 5. This is according to T11, T13, and K11 in the figure below, and the reason is to help avoid high currents in the return cable which may result in noise.
For the return wires from external devices such as T13 and K11, use separate wires that are connected at the RET terminal.
Terminals 3, 4, and 5 together act as an internal ground rail that is internally connected to all local grounds such as RET.
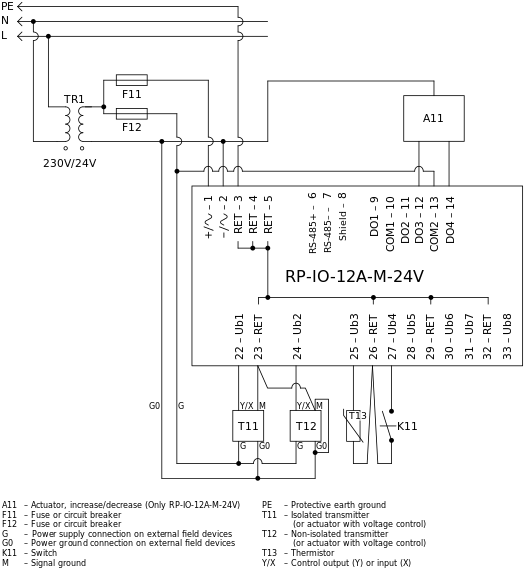
The fuses F11 and F12 may be combined into a single fuse (circuit breaker), but the recommendation is to use two separate fuses (circuit breakers).
It is important to know that several nodes are internally interconnected to the common signal ground. This is important for safety reasons and to help avoid ground loops and incorrect supply of G0. The following nodes are all interconnected:
All RET terminals (3, 4, 5, 23, 26, 29, and 32)
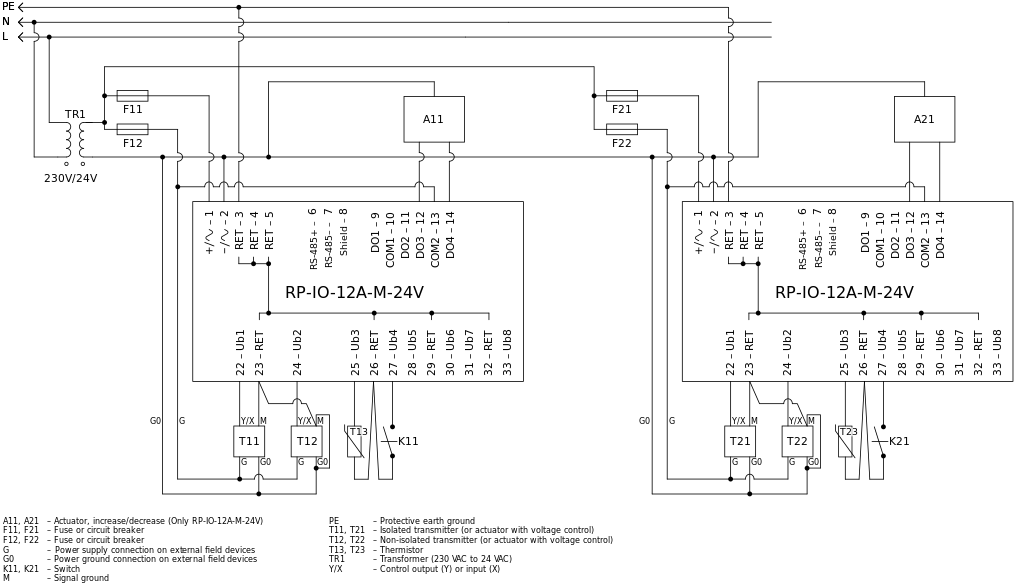
Powering more than one RP-IO module from a common transformer is acceptable when the I/O modules are installed within the same cabinet, or directly adjacent cabinets connected with conduit.
Use the following recommendations to design a good working system:
Use the same recommendations as provided for a system with a local transformer above.
Do not interconnect the RP-IO module and their groups of connected devices, such as actuators and transmitters, beyond what is shown in the figure below to minimize potential problems with ground loops.
It is recommended to use separate fuses (circuit breakers), F11 and F21, for the power supply to each RP-IO module so that a problem with one RP-IO module does not affect another RP-IO module.
If you use a common fuse (circuit breaker) for two RP-IO modules, and there is a problem with one of the I/O modules, the troubleshooting may be more difficult.
It is recommended to use separate fuses (circuit breakers), F12 and F22, for the power supply to actuators and transmitters connected to different RP-IO modules so that a problem with an actuator or transmitter connected to one RP-IO module does not affect an actuator or transmitter connected to another RP-IO module.
The RP-IO modules use BACnet MS/TP for communication over an RS-485 bus. Use the following recommendations to configure the RS-485 electrical interface between the I/O modules and the automation server that hosts the MS/TP (RS-485) bus and the I/O modules.
Proper communication on the BACnet MS/TP (RS-485) bus between I/O modules and the automation server is dependent on a common ground reference at each device. The common reference must not differ from the other MS/TP devices by an amount that exceeds the common-mode voltage tolerance of the RS-485 transceivers. The ground connection to terminal 3 is dependent on providing a solid ground path for transient suppression, but also to help avoid common-mode voltage differences between I/O modules and also the automation server that hosts the I/O modules. A difference of 0 volt is preferred but a difference of less than +/- 1 or 2 volts is needed. The shielded twisted pair cable used for the MS/TP (RS-485) bus is recommended to have the shield connected to earth ground at only one location and that connection is recommended to be at the automation server hosting the MS/TP (RS-485) bus. The shield should be spliced through at each I/O module location. This shield offers a good reference to measure any ground voltage differences at each MS/TP node. Using the MS/TP cable shield as the reference, measure the voltage seen on the I/O module (terminal 3 or RET) to determine the ground difference from the MS/TP (RS-485) bus. For more information, see RS-485 Communications .
The Shield terminal on the I/O module's RS-485 terminal block is a convenience terminal intended to be used to interconnect two shield drain wires. There is no electrical connection in the I/O module.
 I/O Wiring
I/O Wiring
 Grounding and Power
Grounding and Power
 RP-IO Modules
RP-IO Modules
 RP-IO Models
RP-IO Models
 RS-485 Communications
RS-485 Communications