There are four different types of reset for the automation servers: warm start, cold start, reset, and reset to DFU mode. Depending on the type of reset, the automation server can be reset using the reset button or a command from WorkStation.
action_zoom_plus_stroke

Imagem:
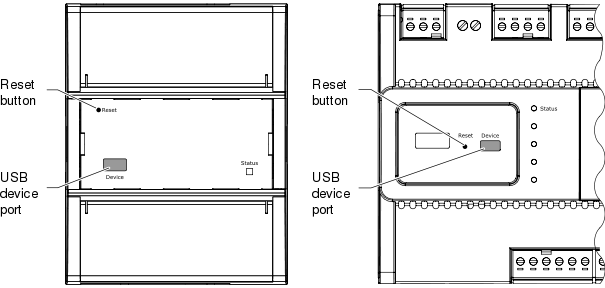
Location of reset button and USB device port on different server models
You can use a straigthened segment of a paper clip or a similar tool to press the reset button.
Tabela: Automation Server Reset Functions
|
Type
|
Triggered by
|
Description
|
Variable values
|
Configuration, Historic database
|
IP settings
|
|
Warm start
|
Command from WorkStation
|
Stops the automation server application and then restarts the application.
|
Affected according to the configured retain levels for the variables
|
Retained
|
Retained
|
|
Cold start
|
Command from WorkStation
|
Stops the automation server application and then restarts the application.
|
Affected according to the configured retain levels for the variables
|
Retained
|
Retained
|
|
Reset
|
Short push on Reset button
Power return
|
Stops the automation server application and the operating system and then restarts the operating system and the application.
|
Affected according to the configured retain levels for the variables
|
Retained
|
Retained
|
|
Reset to DFU mode
|
3 pushes on Reset button within 2 seconds
|
Puts the automation server into DFU mode, which enables Device Administrator to communicate with the server.
|
Not applicable
|
Not retained
|
Not retained
|
Parameters and variables that are used to define the system or contain important data in the automation server can be retained in a permanent memory. These parameters and variables are automatically saved in the event of power failure, or request for restart and are reloaded after startup.
You can define what kind of events that retention for the parameters and variables should apply.
Retain Levels for Variables
Variables have a configurable retain level, which controls if the value of the variable is retained after a restart of the automation server. There are three retain levels:
The following table lists what is retained after a warm start, cold start, or reset based on the configured retain level.
Tabela: Retained Variable Values Depending on Reset Type and Retain Level
|
Reset type
|
Retain level:
No
|
Retain level:
Warm start
|
Retain level:
Cold start
|
|
Warm start
|
Default value
Values configured by a user or application are lost.
|
Variable retains last value configured by a user.
Values configured by an application are retained.
|
Variable retains last value configured by a user.
Values configured by an application are retained.
|
|
Cold start
|
Default value
a
Values configured by a user or application are lost.
|
Variable retains last value configured by a user.
Values configured by an application are lost.
|
Variable retains last value configured by a user.
Values configured by an application are retained.
|
|
Reset
|
Default value
a
Values configured by a user or application are lost.
|
Variable retains last value configured by a user.
Values configured by an application are retained.
|
Variable retains last value configured by a user.
Values configured by an application are retained.
|
Para mais informações, consulte Retain Level
.
Configuration and Historic Database
A number of parameters describe the current configuration. The historic database contains information collected from different sources. Parameters and historic database are retained at both Warm and Cold start.
DFU Mode
The Device Firmware Upgrade mode can be used if the automation server does not communicate in its normal operating mode. In the DFU mode, with a PC connected to the USB device port on the automation server, the Device Administrator can be used to update the firmware.
Para mais informações, consulte Resetting an Automation Server to DFU Mode
.

 Automation Server Reset Functions
Automation Server Reset Functions
 Connecting to an Automation Server Using the USB Device Port
Connecting to an Automation Server Using the USB Device Port
 Uploading and Upgrading an Automation Server
Uploading and Upgrading an Automation Server
 Downloading an Upgraded Database to an Automation Server
Downloading an Upgraded Database to an Automation Server
 Getting Automation Server Debug Information
Getting Automation Server Debug Information
