You configure communication parameters when you add a SmartStruxure server. The Enterprise Server distributes the communication parameters to the SmartStruxure server devices so that they know how to communicate with the newly added SmartStruxure server.
Communication Parameters
Communication parameters include address, protocol, and port. You configure these parameters in the Server wizard when you add a SmartStruxure server.
Address
Every SmartStruxure server needs an IP address to communicate in the network. You either use the installation default IP address, or specify a static address that is unique in the network. We advise against using DHCP for any SmartStruxure server that contains a BACnet Interface.
You can also specify the SmartStruxure server's fully qualified domain name, if one is defined and the DNS service is enabled. A fully qualified domain name for a server consists of two parts: the host name and the domain name. For example, a server with a host name “es1” and the domain name “universityx.edu” has the fully qualified domain name “es1.universityx.edu”. Always use the SmartStruxure server's fully qualified domain name, rather than its host name (without the domain information), to avoid server communication problems with lead-shadow relationship.
For more information, see Lead-Shadow Reference SmartStruxure Server Communication Problems
.
Protocols
SmartStruxure servers can use three different communication protocols:
TCP is fast and you can set up domain authentication which makes for easy, yet secure access.
HTTP is slower than TCP but better for accessing resources outside the LAN/firewalls.
HTTPS is slower than HTTP but safer for accessing resources outside the LAN/firewalls.
Ports
Each SmartStruxure server listens on three communication ports, one for each communication protocol:
SmartStruxure Server Communication Parameters
The communication parameters of a SmartStruxure server tell other SmartStruxure servers where and how to communicate with that particular SmartStruxure server. You use different tools to specify, view, and change communication parameters.
action_zoom_plus_stroke
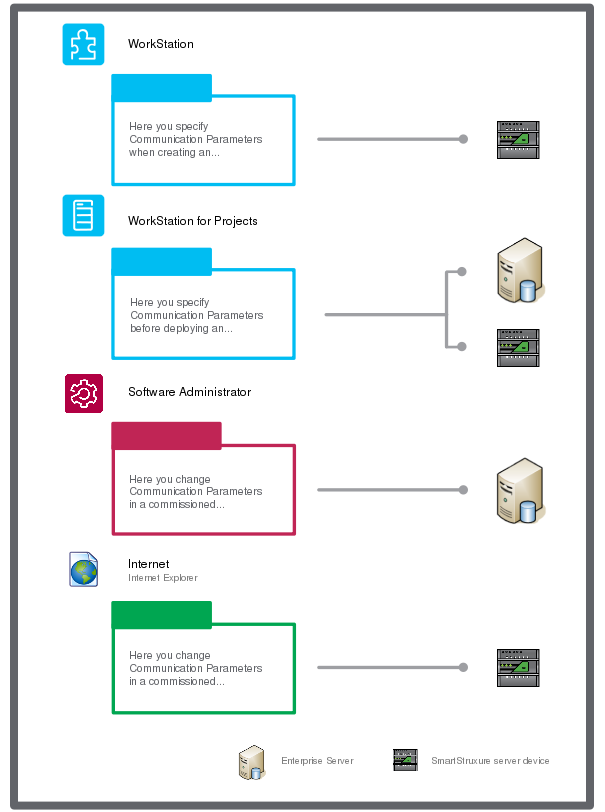
Figure:
Different ways of accessing communication parameters
To change the communication parameters of an Enterprise Server after it has been commissioned, you need to open the Software Administrator application. In the Software Administrator, you must first stop the Enterprise Server before configuring the parameters.
To change the communication parameters of a SmartStruxure server device after it has been commissioned, you need to access it through the web interface.
SmartStruxure Server-to-Server Communication Parameters
Each SmartStruxure server maintains a list of all the other SmartStruxure servers in the system and the communication parameters of those SmartStruxure servers.
action_zoom_plus_stroke
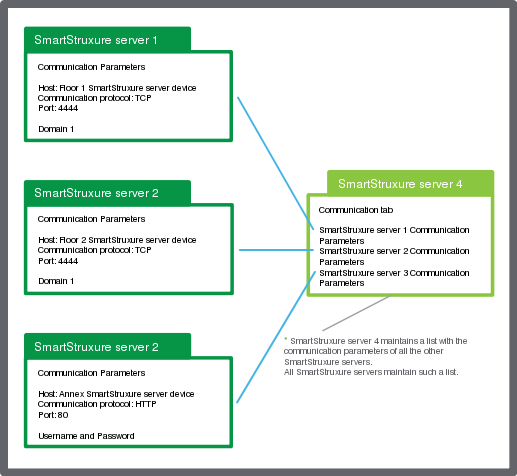
Figure:
Keeping track of the other SmartStruxure servers
In WorkStation, you can select a SmartStruxure server in the System Tree pane and view its communication parameters in the Network tab of its properties. In the Communication view, you can view the information the SmartStruxure server has about the communication parameters of other SmartStruxure servers in the system. Each SmartStruxure server needs to know where and how to address other servers.
When a SmartStruxure server device is added, its communication parameters are distributed by the Enterprise Server to all other SmartStruxure servers in the system. Every SmartStruxure server’s communication parameters end up in the Communication view of every other SmartStruxure servers.
However, if you change the IP address or protocol port number in an already commissioned SmartStruxure server, you must manually update this information in the Enterprise Server Communication view. The Enterprise Server then distributes the new parameters to the other SmartStruxure servers.
SmartStruxure Server Communication in Project Configuration Tool
When you create a new virtual SmartStruxure server, the communication settings are already filled in, such as on-site IP and communication ports. However, the on-site IP address has to be configured in Project Configuration Tool before you deploy all servers to a site with a functional IP network.
For more information, see SmartStruxure Server Communication in Project Configuration Tool
.
Email Server Settings
Some Building Operation features, alarms in particular, can be configured to send emails to notify users about important events.
For example, if an alarm is triggered, the SmartStruxure server notifies the email recipient specified in the alarm. The SmartStruxure server sends the email through the email server. The Sender email specified on the SmartStruxure server is also the receiver of the replies from the email recipient.
You select and specify a primary email server for email communication. You can also specify a secondary email server in case the connection to your primary choice fails.
The SmartStruxure server tries to connect to the primary email server, and then to the secondary if the primary fails, and then to the primary again, and so on.
You can test email settings by using the Schneider Electric Test Email Server Settings. The Schneider Electric Test Email Server is hosted by Schneider Electric for test purposes and is available for Building Operation customers. The maintenance on this server is limited so it might be disconnected from time to time.
For more information, see Using the Schneider Electric Test Email Server to Test Email Notifications
.
When sending emails, you can send them not encrypted or encrypted using either the TSL or the SSL protocol. You can select one method for the primary email server and another method for the secondary email server. The Schneider Electric Email Server does not support encrypted emails.
When logging on to the email server, the user is authenticated using an authentication protocol. If no user name is specified, no authentication protocol is specified. If a user name is specified, the SmartStruxure server tries to authorize the user using the CRAM-MD5 protocol. If the first authentication fails, the SmartStruxure server tries to authorize the user using the LOGIN protocol using the CRAM-MD5 protocol.


 SmartStruxure Server Communication
SmartStruxure Server Communication
 Enterprise Server Properties – Email Tab
Enterprise Server Properties – Email Tab
 SmartStruxure Server Device Properties – Email Tab
SmartStruxure Server Device Properties – Email Tab
 Email Notification Distribution Method
Email Notification Distribution Method
 Selecting and Specifying an Email Server for Email Notifications
Selecting and Specifying an Email Server for Email Notifications

